Initialization:
-
Channel acquisition: Upon initialization or after recovering from signal loss, the station should acquire a downstream channel, by scanning the downstream frequency band until it finds a valid one of 802.14
-
physical level synchronization to align the bit stream
-
Ranging and power leveling: Because of large propagation delay, each station must learn its range from the headend and compensate for this range such that the station and the headend have a consistent system-wide view of time to synchronize the MAC operations. This process is known as ranging.
-
A station with data to transmit must send a request for bandwidth on the upstream channel to the headend station.
Normal Operation:
IEEE 802.14 uses a channelized approach:
-
Up to two thousand stations are connected to a single tree network.
-
Utilizes frequency division multiple access (FDMA) in downstream and upstream communication channels.
-
Each FDMA channel is further slotted by time division multiple access (TDMA) on the upstream channel dividing them into fixed-sized time intervals called minislots.
-
Stations send transmission requests, known as packet data units (PDUs) to the headend in a single minislot called a contention slot. These are also known as bandwidth requests. These slots are prone to collision when more than one station attempts to transmit a request in the same slot.
-
Stations send data in data slots, which consist of multiple minislots. These are allocated by the headend so they are collision-free.
- The duration of one minislot is equal to the time required to transmit 8 bytes of data and other overhead.
- The size of a minislot is designed to carry a PDU.
- Each minislot has an integer indentifier, called the minislot number, which is 16 bit wide, assigned by the headend.
- When the minislot number counts to its maximum value, it starts the count over again at zero.
- Stations and the headend both recognize the minislot number.
The headend station transmits feedback and data to the stations using a downstream channel. The system of upstream and downstream transmission channels are asymmetrical with typical upstream and downstream rates equaling approximately 0.5-10 Mbits/sec and 30 Mbits/sec respectively. The IEEE 802.14 MAC is only concerned with the transmission of data on the upstream channel.
Using the downstream channel, the headend acknowledges the request or indicates that a collision has occurred. The latter initiates the collision resolution process. Once the collision is resolved, the headend station sends a message to the station granting the use of the upstream channel. Because bandwidth is allocated by a reservation process, no collisions will occur during the transmission of data. Only transmission requests, which are transmitted in contention slots, are subject to collisions.
To reduce the bandwidth wastage due to collisions, stations send small request PDUs, which are subject to collisions, to the headend which then in turn schedules the requests and informs stations in the downstream channels, so that their upstream data slots can be sent collision free. Access delay can be reduced if most of the requests are piggybacked instead of having stations using contending minislots. A specific field in the header of the upstrem data slot is reserved for the purpose of a piggyback. So in this way, a station can send its bandwidth request through piggybacking on the collision-free data slot.
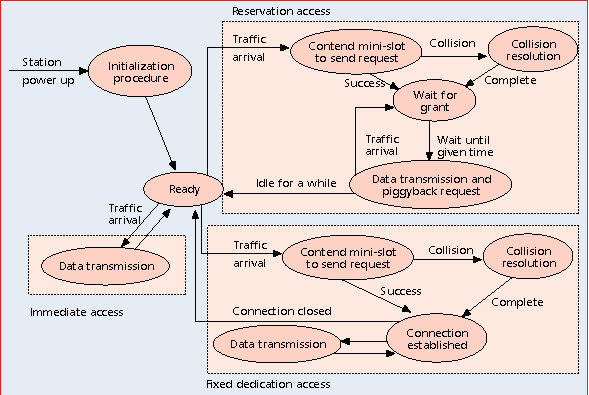
(Station state diagram)
There are two places in the HFC network where collisions could occur:
-
ranging responses
- bandwidth requests
Collision resolution scheme for the MAC:
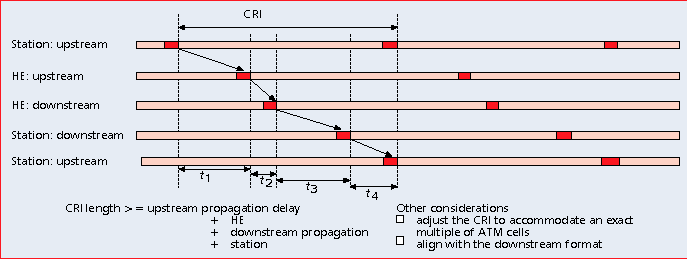
(collision resolution interval (CRI))
The collision resolution algorithm in IEEE 802.14 consists of two parts. The first part is the first transmission rule which is designed for newly arriving requests and the second part is the retransmission rule which is designed for collided requests.
The first transmission rule exercises the priority control, to allocate groups of minislots of different varying priorities. It also uses a FIRST-IN-FIRST-OUT (FIFO) mechanism to block requests that are too young.
Retransmission:
- The protocol is based on a blocking ternary tree splitting algorithm.
-
Tree splitting algorithms have been used in the past to improve the performance of collision access.
-
In a tree splitting algorithm, all stations that are involved in a collision split into a number of subgroups. After a collision, only the stations in the first subgroup continue the collision resolution step. The stations in the second subgroup resume the collision resolution process after all stations in the first group have successfully transmitted and so forth.
-
A ternary tree splitting algorithm always divides colliding stations into three subgroups. Some tree splitting algorithms are non-blocking, which allows stations to transmit new requests at any time.
-
Blocking tree-splitting algorithms do not allow new stations to transmit during an ongoing collision resolution process.
-
The selection of a blocking algorithm for 802.14 is intended to reduce the MAC access delay variance.
Media Access Control in the HFC Network