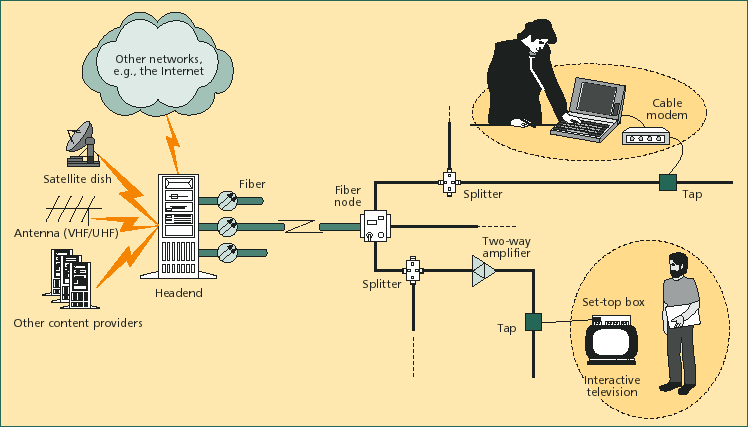
A hybrid fiber coaxial (HFC) network is a telecommunications technology in which optical fiber cable and coaxial cable are used in different portions in a network to carry broadband content. The telecommunications industry is using this technology in new and upgraded networks to provide better multimedia interactive services, such as video-on demand, high quality videophone, and high-speed Internet access.
Using HFC, fiber optic cable is installed at the headend, or distribution plant, to serving nodes. The signals are then distributed to users within the serving area of the node by amplified tree-and-branch feeder coaxial cables. There are downstream channels(headend to stations) and upstream channels(stations to headend).
A multiple access control (MAC) protocol must be used to control the data communication between the stations and the headend, specifically the upstream communication in order to efficiently use this channel. The MAC specifies the rules that the station must abide by in order to gain access to this channel.
An HFC network