...................................................................................................................................................................................
The Routing Information Protocol (RIP) was one of the earliest intra-AS
Internet routing protocols and is still in widespread use today. It traces
its origins and its name to the Xerox Network Systems (XNS ) architecture.
The widespread deployment of RIP was due in great part to its inclusion in
1982 of the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) version of UNIX supporting
TCP/IP. RIP version 1 is defined in RFC 1058, with a backward- compatible
ver.2 defined in RFC 2453.
Now recall the distance vector (DV), and look at its features.
DV algorithm is iterative, asynchronous and distributed one;
- It is distributed in that each node receives some information
from one or more of its directly attached neighbors performs a calculation,
and may then distribute the results of its calculation back to its neighbors.
- It is iterative in that this process continues on until
no more information is exchanged between neighbors.
- This algorithm is asynchronous in that it does not require
all of the nodes to operate in lockstep with each other.
RIP is a Distance Vector protocol
that operates in a manner very close to the idealized protocol, which allows
neighboring routers to exchange the routing information with each other. The
features of RIP are as follows;
- RIP for IPv4 ; RFC 1058/1721/1722/1723/1724
- RIP for IPv6 ; RFC 2080
- Routed in BSD, SunOS
- Maximum hopping; 15
- Cold-Start ; It takes at most 450s(=15x30 ) for calculate.
- Exchange Distance Vector database (routing table) information
every 30 sec.( using UDP port 520)
->transfer about the condition change of node/link
- If there is no response for 180 sec, the network is down
(keep-alive)
Expression for Minimum Distance Path;
D(i,j) ; distance vector
d(i,j) ; distance between node_i and node_j
D(i,j) = min [d(i,k) + D(k,j)] (for all k)
|
Bellman-Ford's algorithm was developed by Xerox-PARC as XNS-RIP. It defines
the optimum path to the destination; minimum distance and attribute distance
vector information. This algorithm is mathematically expressed as following
table.
||Prev
||Next
||
(c) Marcos Andres Diaz & Yasuko Iwai
Boston University,
College of Engineering
|
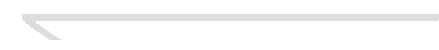
|
 Bellman-Ford's Algorithm (Mathematical Approach)
Bellman-Ford's Algorithm (Mathematical Approach)