FDDI Specifications
FDDI is not just one, but four specification pertaining to the Physical and Media Access layers of the OSI model. FDDI is similar to IEEE 802.3 Ethernet and IEEE 802.5 Token Ring in its relationship with the OSI model. The four specifications, as shown below are, MAC layer spec, Physical layer spec, Physical medium dependent spec, and the Station Management spec.
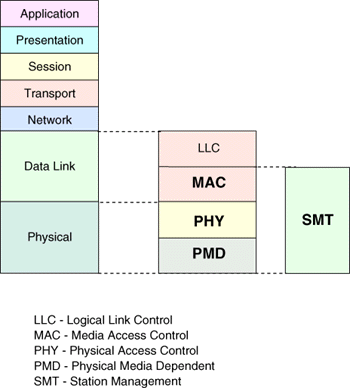
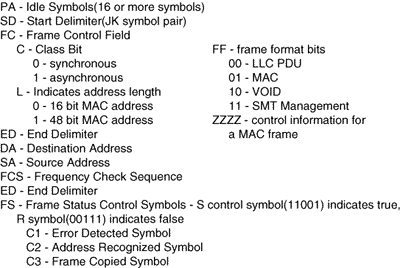
- The MAC layer is responsible for address checking, error detection, measuring the TRT (Token Rotation Time), and calculating the THT (Token Holding Time).
- The LLC layer serves the same function as it does in Ethernet and Token Ring which is to encapsulate layers 3-7 into the LLC layer's data transfer format
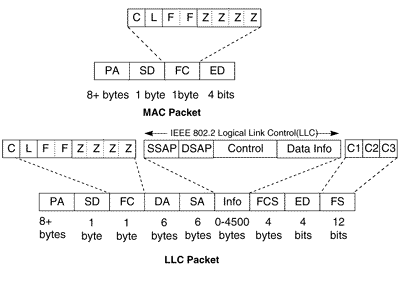
The MAC and LLC packets used in FDDI are shown below, followed by a description of the fields within each packet. The MTU of FDDI is 4352 octets is needed to provide means to transmit IP or ARP over FDDI
A description of the fields in each of the packets:
- The physical media described by the FDDI specifications are various optical fibers with some of the following characteristics:
FDDI Physical Parameters
- Data Rate: 100Mbps.
- Topology: physical ring of trees, logical ring.
- Maximum distance between adjacent stations: 2 km.
- Total max. ring length: 100 km.
- Max. number of attached stations: 1000.
- The Station Management layer of the specification deals with measuring frame statistics, detecting signal loss and ensuring that workstations are connected properly
- The Physical Media Dependent link converts electrons to light for transmission across fiber
FDDI Definitions
- TRT - Token Rotation Time - the amount of time it takes the token to traverse the ring
- THT -Token Holding Time - the amount of time a station can hold the token
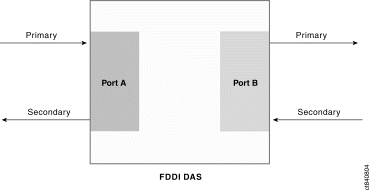
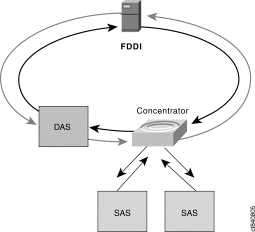
- SAS - Single-Attachment Station - attaches to only one ring, cannot connect directly to the ring, must be attached through a concentrator
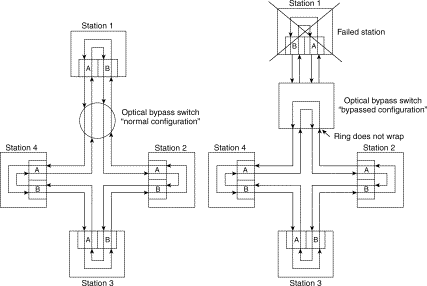
- DAS - Dual-Attachment Station - attaches to both rings, must be up and running at all times
- SAC - Single-Attached Concentrator - attaches a station to only primary ring
- DAC - Dual-Attached Concentrator - is a dual-attachment device that guarantees a single attachment device will not disrupt the ring function if it is powered down or fails
- Bypass Switch - provides continuous dual-ring access in the event a device fails
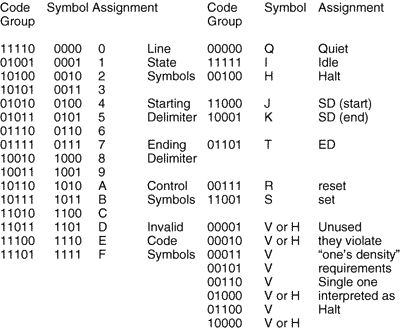
On the physical layer, FDDI uses Non Return to Zero Invert (NRZI) data encoding scheme to generate the signal representing 4B/5B encoding bits onto the ring. This prevents continuous 0's from being passed around the ring