What is FDDI?
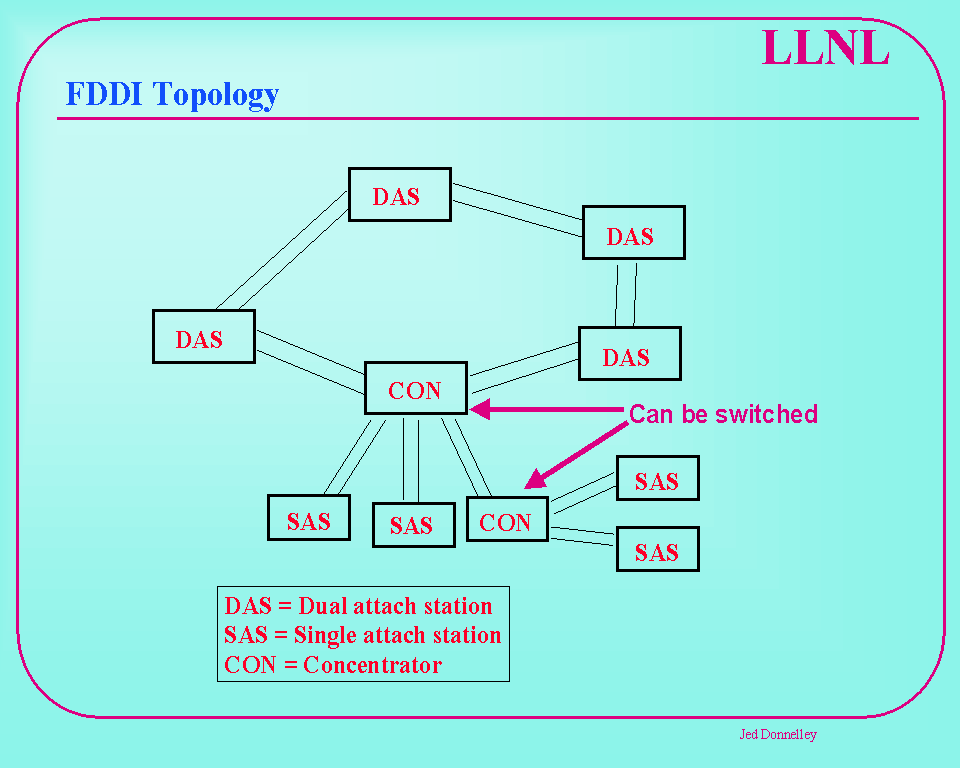
FDDI is a highly reliable way to transmit data using a dual-ring protocol based on the token ring protocol. A token ring network is a local area network where all the computers on the network are connected in a giant circle and a token-passing setup is employed to prevent data collision when two computers send data at the same time. FDDI uses two rings that are independent of each other and transmit data in opposite directions. A secondary ring provides an alternate data path in the event a fault occurs on the primary ring. FDDI stations incorporate this secondary ring into the data path to route traffic around the fault. During normal operation, the primary ring transmits data and the secondary ring is idle. Here is a sample FDDI topology. Click on the image for definitions.
Where is FDDI used?
FDDI is used mainly in mission critical and high traffic networks where large amounts of data flow need to flow quickly and efficiently. FDDI is used anywhere that utilizes a large network in need of high bandwidth. Businesses, the Government, hospitals and other medical fields, stock exchanges and money markets, the automobile industry, and the media, just to name a few. It has become the mainstay access method of high speed networking in local area and metropolitan area networks in many places.
Why use FDDI?
FDDI offers more powerful workstations and servers, intensive network applications, growing distributed client/server applications, larger spans of distributed networks, increasing numbers of network users, and bigger and more powerful software applications. Also, FDDI offers higher capacity and performance with more simultaneous transactions, higher availability due to the dual ring topology, and longer distance loops, up to 100km. It is also compatible with other protocols that follow the OSI model, so integration with most existing and new technologies is seamless.
The future of FDDI...
A newer version of FDDI, called FDDI-2, supports the transmission of audio and visual information as well as data. Another version, FDDI-Full Duplex Technology or FFDT, uses the same network setup as FDDI but can support twice the data rate, or 200 Mbps.