By summing Theorem 2.7 over many iterations, we may
obtain a lower bound on the length nm of the m-th code
of any minimal G-family.
Proof. Consider summing a weaker inequality obtained from
Theorem 2.7
by eliminating the floor function. Summing over iterations
1...m of the G-construction we get:
Noting that for trivially seeded codes,
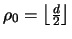 and
and
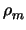
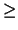 0, we may reduce this to:
0, we may reduce this to:
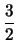
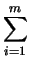
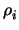
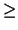 m
m(
d - 2) -
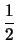
(
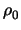
-
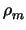
)
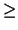 m
m(
d - 2) -
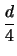
Furthermore, since we are dealing with minimal G-codes,
so that we may now conclude the proof:
nm =
md -
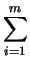
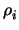
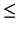 md
md -
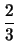
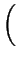 m
m(
d - 2) -
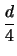
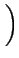
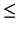
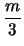
(
d + 4) +
width4pt depth2pt height6pt
In the case of a G-family seeded by a non-trivial code of length
n0 and covering radius 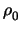 , Corollary 2.11 may
be easily generalized to:
, Corollary 2.11 may
be easily generalized to:
Clearly, Corollary 2.11 applies to all lexicodes and
trellis-oriented lexicodes. It is a asymptotically tighter than the
similar bound given by Brualdi and Pless [9, Theorem3.5]:
k 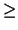 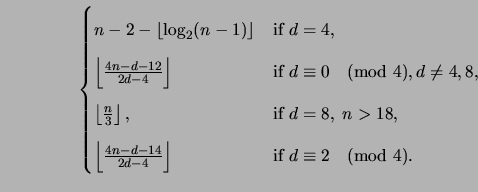 |
(9) |
Specifically, Corollary 2.11 asymptotically binds
k 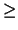 3
3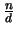 whereas Equation (2.14) binds
k
whereas Equation (2.14) binds
k 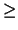 2
2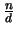 . Nevertheless, both of these bounds are weak as
illustrated by Appendix A.1.
. Nevertheless, both of these bounds are weak as
illustrated by Appendix A.1.
http://people.bu.edu/trachten
![]() , Corollary 2.11 may
be easily generalized to:
, Corollary 2.11 may
be easily generalized to:
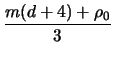 +
+